Banking security has never been more critical. As cyber threats grow in sophistication, banks must stay ahead of attackers who exploit outdated systems and evolving fraud tactics. Traditional security measures struggle to keep pace, making artificial intelligence (AI) an essential tool for risk management.
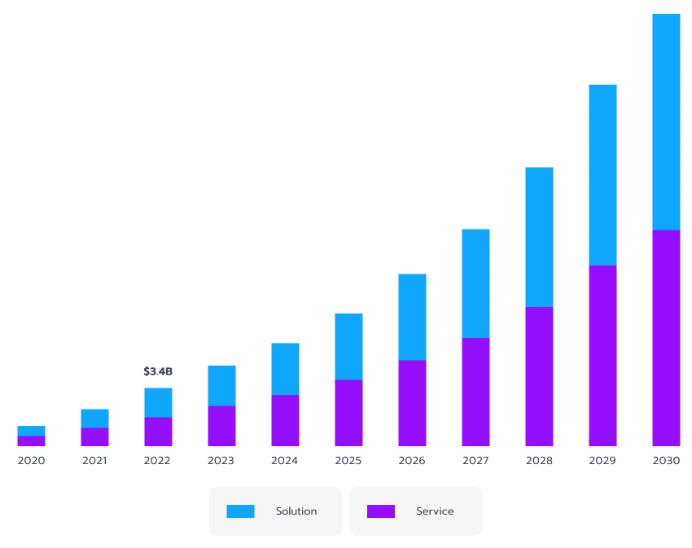
AI’s role in banking has expanded rapidly, with financial institutions investing in advanced machine learning models to detect fraud, strengthen data privacy, and streamline compliance. The market for AI in banking has seen significant growth and is expected to continue expanding (see Fig. 1). According to the U.S. Department of Treasury, many global banks have already experimented with AI-based systems to enhance security, demonstrating a shift toward technologies that process vast amounts of data, detect hidden patterns, and improve overall resilience.
As we enter Q2 in 2025, AI is poised to play an even greater role in safeguarding financial transactions. The question isn’t whether AI will shape banking security – it’s how effectively banks can use it to outmaneuver emerging threats. Let’s explore AI’s impact on fraud detection, privacy protection, and regulatory compliance.
Figure 1. The U.S. Artificial Intelligence in banking market size
AI-powered fraud detection
Financial institutions process vast numbers of transactions daily, making it difficult for traditional security tools to identify fraudulent activity before it causes harm. AI-driven fraud detection systems address this challenge by analyzing real-time transaction data, spotting unusual patterns, and comparing them against past behavior.
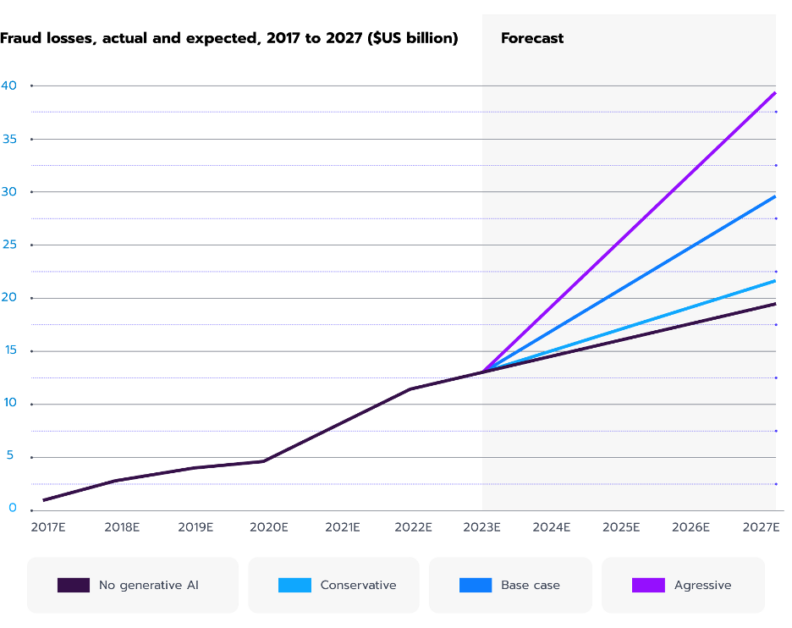
Generative AI is now adding a new layer of complexity to financial fraud. According to the Wall Street Journal, deepfakes have become a growing concern in banking, making scams harder to detect and increasing fraud-related losses (see Fig. 2). This underscores the double-edged nature of AI – it can be both a weapon for cybercriminals and a powerful tool for fraud prevention.
On the defensive side, AI helps investigators focus on high-risk cases rather than sifting through thousands of false positives. Machine learning models can detect subtle signs of suspicious activity, such as abnormal login attempts, rapid transactions from multiple locations, or device-specific anomalies. These early warnings allow banks to intervene before fraud escalates.
As fraud tactics evolve, so does AI. Banks that invest in deep learning technologies can stay ahead of cybercriminals, reducing financial losses and protecting their reputations. AI-driven fraud detection is no longer just an option – it is becoming a necessity in modern banking security.
Figure 2. Generative AI increasing fraud losses
Protecting customer data and privacy
Data privacy regulations are becoming stricter each year. One of the most recent, the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), went into effect just weeks ago, reflecting growing concerns about cybercriminals targeting sensitive financial data. The rising number of data breaches across industries underscores the urgency of stronger security measures (see Fig. 3).
A single data breach can result in hefty fines and a loss of customer trust. AI can strengthen data security by continuously monitoring how sensitive information is accessed and used within an organization. Instead of relying on manual oversight, AI-powered systems detect unusual behavior in real time, flagging potential threats before they escalate.
Banks can also implement AI-driven risk scoring systems that assess each data request based on factors like user behavior, location, and device type. If a request falls outside normal parameters, the system can trigger an alert or block access until further review. According to an IBM report, financial institutions using AI-powered monitoring tools have reduced response times to privacy threats by nearly a third.
As more customers shift to digital banking, the need for robust data protection has never been greater. AI is helping financial institutions stay ahead of cybercriminals, ensuring compliance with evolving regulations while reinforcing customer confidence in their digital transactions.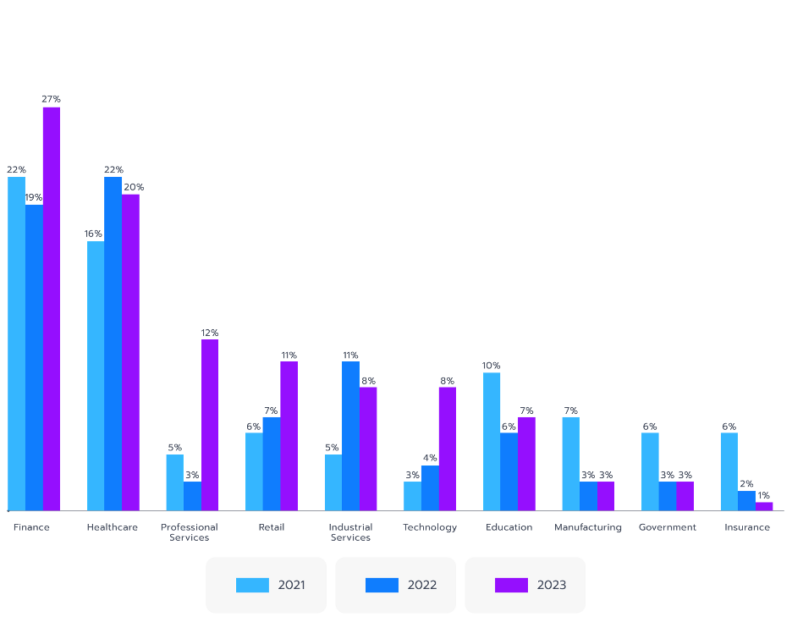
Figure 3. Percentage of data breaches by industry
Strengthening compliance and AML efforts
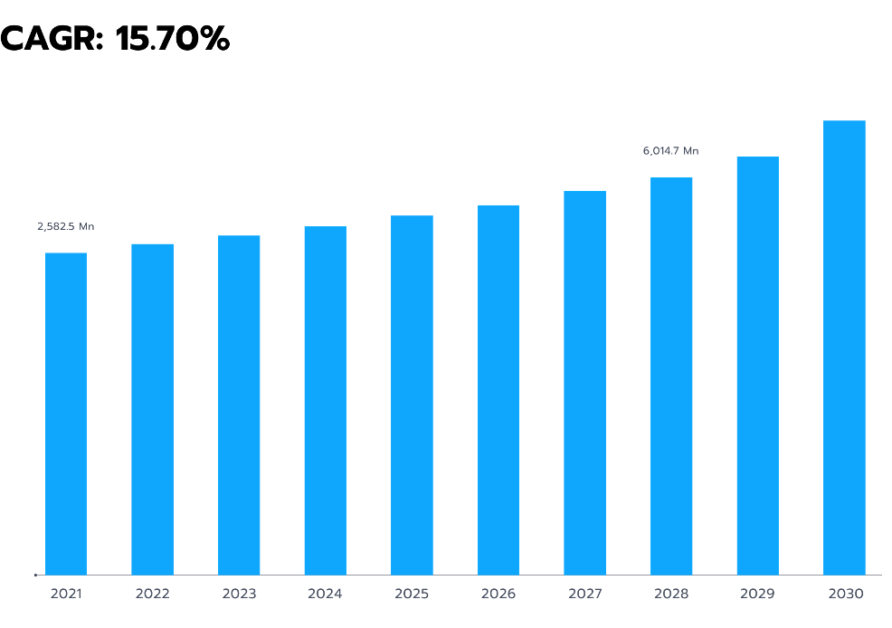
Money laundering has long been a challenge for the banking sector, prompting governments to impose increasingly stringent compliance requirements. Banks must detect illicit transactions that often blend seamlessly with legitimate financial activity. At the same time, the global market for anti-money laundering (AML) systems continues to grow (see Fig. 4).
AI enhances AML efforts by analyzing vast amounts of data faster and more accurately than traditional manual reviews. According to a 2024 EMEA AML Survey by PwC, top financial institutions have reduced compliance costs by up to 15 percent by integrating AI into their AML processes.
AI-powered systems monitor transactions for complex patterns that may indicate money laundering, such as sudden spikes in transaction volume, international transfers with no clear business purpose, and repeated deposits followed by rapid withdrawals. These systems can also cross-reference multiple data sources, including public records and watchlists, to flag individuals or organizations with a history of financial misconduct.
By automating key parts of the compliance process, AI allows financial institutions to focus on high-risk cases rather than getting overwhelmed by false positives. This not only improves regulatory compliance but also reduces the backlog of potential violations, ensuring a more proactive approach to financial security.
Figure 4. Global anti-money laundering market
AI’s broader influence on banking security
Fraud detection, data protection, and compliance are just part of AI’s growing role in financial security. Advanced AI models are transforming nearly every aspect of banking, from customer onboarding to credit scoring. These systems pull data from multiple sources—web platforms, mobile apps, and even social media—to assess risk in near real-time. According to the Global Finance & Banking Review, AI-driven analytics have improved investment predictions by 45 percent.
AI is also helping banks anticipate emerging threats. As cybercriminals develop more sophisticated tactics, AI-powered tools can analyze patterns and predict potential attack methods before they become widespread. This proactive approach reduces last-minute crisis management, allowing banks to implement stronger defenses in advance.
As AI capabilities continue to expand, financial institutions must balance innovation with responsible use. AI offers immense potential for improving security, but its effectiveness depends on thoughtful implementation and ongoing oversight. Banks that embrace AI-driven security strategies will be better positioned to protect their customers, comply with regulations, and maintain trust in an increasingly digital financial landscape.
Final thoughts
AI is reshaping banking security, helping financial institutions protect assets, reduce fraud, and strengthen customer trust. From fraud detection and automated compliance checks to predictive analytics, AI-driven systems are reducing guesswork and enhancing risk management.
In 2025, AI-powered security measures are expected to become standard in leading banks, helping them safeguard sensitive data and meet regulatory demands. When banking organizations implement AI responsibly, AI can not only mitigate risks but also lay the foundation for a more secure and resilient financial industry.
The post How AI Is Changing Banking Security and Risk Management appeared first on Unite.AI.